Cervical, Endometrial & Ovarian Cancer
There are four major cancers among women. Besides breast cancer, the other three common female cancers are cervical, ovarian, and endometrial cancers. These four cancers are showing high prevalence in Malaysia.
Among these four types of cancers, other than breast cancer and cervical cancer, of which they can be prevented and detected early through breast cancer screening and pap smear examinations, both ovarian and endometrial cancer are not preventable, since general examinations are not able to detect these two types of cancers easily and early.
Although there is innumerable information about these four types of cancer, many women are still confused about what needs to be done, at what ages they need to do their examinations, and whether there is any need to do examinations in the first place.

Cervical Cancer
To do examinations at the right time
Cervical cancer is the most common cancer related to female reproductive organ. It is often detected among middle-aged women approximately 50 years old. The most common method of examination is pap smear, which is an effective method of preventing cervical cancer, especially to those women who are still active sexually.
In some European and American countries, such as Finland and Sweden, their policies requiring all female citizens doing cervical cancer screening, and the government will provide pap smear tests to all females in these countries. Through this mandatory examination program, both countries have successfully reduced the incidence rate of cervical cancer as well as its mortality.
In fact, Europe and the United States have different recommended ages for conducting cervical cancer screening. In Europe, it is recommended that invasive examinations to be performed between ages of 35 and 60, and non-invasive examinations should be performed between ages of 25 and 35. After that, the examination should be repeated at intervals of 3 to 5 years. In other words, European countries recommend that women should start cervical cancer screening from age of 25.
In the United States, it was recommended that cervical cancer should be examined at the age of 18. Moreover, this examination is suggested to be performed every year.
To do pap smear after sexually active
However, in Malaysia, no cervical cancer screening plan has been established and public needs to bear the costs on their own. Therefore, there is no recommended age of getting pap smear. Generally, it is recommended that this test only begins when a female is sexually active, with the test’s interval ranging in between 2 to 3 years. Should any abnormal symptoms are found, then pap smear should be done once every six months.
As for women who do not have a sexual life yet, they may not need to do any examination. Alternatively, they can choose to do a low-invasive examination instead.
The most basic check for preventing cervical cancer is done via pap smear screening, but many people do not know that choosing the right time for doing pap smear is vital for improving the accuracy of this test. The suitable time of this examination is falling into 10 to 20 days, in between menstrual cycles.
Pap smear examination is divided into two types respectively, namely sim pap and thin pap. Actually the same examination method is applied, however the devices of collecting samples are different. The former is developed by the United States. After a sample is taken out, it is put into a container with liquid reagents and sent to the laboratory for testing. As a result, the probability of bacterial infection becomes lower, thus giving higher accuracy on test results.
The prices of sim pap and thin pap are quite similar. They are usually provided by family doctors. Of course, public can check with doctors before doing this test.
Once pap smear showing any abnormalities, doctors will advise patients to get colposcopy and take biopsy samples for further investigations.
Time which is not suitable for doing pap smear: after menstruation.
Because vagina still contains residual bloods, thus affecting the result. If there is obvious foreign body or growth found on cervix, then biopsy is deemed more appropriate compared to scanning test.
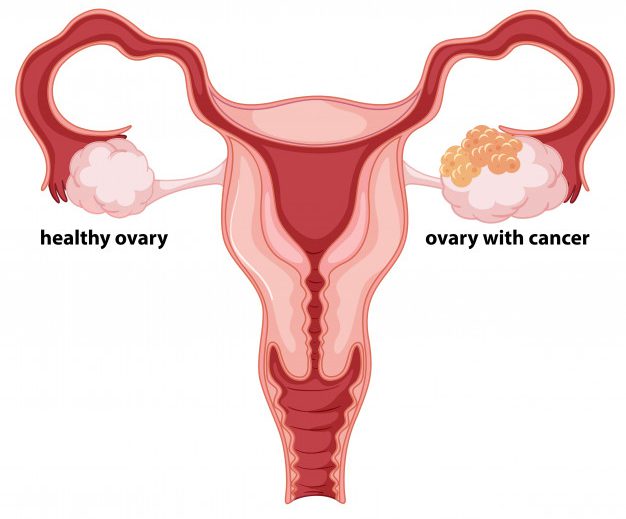
Ovarian Cancer
Examination should be done after 50 years old
Generally, there are no obvious symptoms, so patients are usually found in advanced stage at the time of diagnosis. This situation accounts for 75% of ovarian cancer cases, of which its mortality rate is also very high. The 5-year survival rate is only 28%. However, if this cancer is found early (i.e. stage 1), then the 5-year survival period is as high as 95%.
It is recommended that women over age of 50, should do ovarian cancer tests, because many cases do not have any obvious risk factors. Admittedly, it is difficult to detect ovarian cancer by doing scanning test such as ultrasound. Therefore, ovarian cancer scans are not common. Only in the event of unusual situation, then ovarian examinations are recommended. For examples, blood tests, ultrasound and tumour marker test.
If both ultrasound and tumour marker test showing abnormal results, then doctor will likely recommend biopsy for further investigation.
The reasons why scanning is difficult to detect ovarian cancer
- Ovaries are not easily detected due to location.
- Lack of clear signs of lesions, and the medical history is unclear
- Low prevalence of ovarian cancer requires high-accuracy tools to check and avoid unnecessary intervention
- Lack of effective treatment
- Low efficiency, but high-risk groups can be considered
Hidden symptoms of ovarian cancer
- Lower abdominal pain/compression
- Abdominal enlargement
- Vaginal bleeding
- Urinary tract/intestinal symptoms
Risk factors of ovarian cancer
- Family History: 10% – Familial Ovarian Syndrome
- Not giving birth
- Race and social life
- Smoking
- Hormonal therapy
- Oral contraceptives
Endometrial Cancer
Not many methods for detection
Endometrial cancer is the third most common malignancy of the female reproductive organ. The age of onset is 58 years or older. There are only few detection methods available for this cancer, only pelvic ultrasound and endometrial aspiration (insufficient sampling of menopausal women). Nevertheless, this kind of examination is still considered uncommon.
Risk factors of endometrial cancer
- Not giving birth, irregular menstruation, delayed menopause
- Exogenous estrogen effects.
- Endogenous estrogen effects.
- Diabetes, hypertension, obesity
- Smoking
- Tamoxifen
- Family history
Immediately seek medical attention when abnormal bleeding happens
Among the three major cancers of the female reproductive organ, the screening of cervical cancer is regarded as the most successful program. If regular inspections are performed, cervical cancer can be discovered early, with high chances of getting cured.
Although the standards of pap smears are inconsistent among countries, it is recommended that pap smears to be carried out at regular intervals, say once every or two years. Or women can choose to do a simple pelvic scan once every year or every two years. As for blood tests, tumour markers are required only when the result of pelvic scan is positive, or presence of family history.
On the contrary, scanning test is bringing little effect on ovarian cancer. Hence, tests may only be considered for screening high-risk groups. The same approach applies to endometrial cancer too, of which scanning test is only required for high-risk groups as well.
Since both ovarian cancer and endometrial cancer are cancers that are not easily detectable, they must be examined immediately if abnormal abdominal pain or abnormal bleeding occurs.