Parasitic Worms
Nematodes – Tapeworms, Whipworms, Hookworms
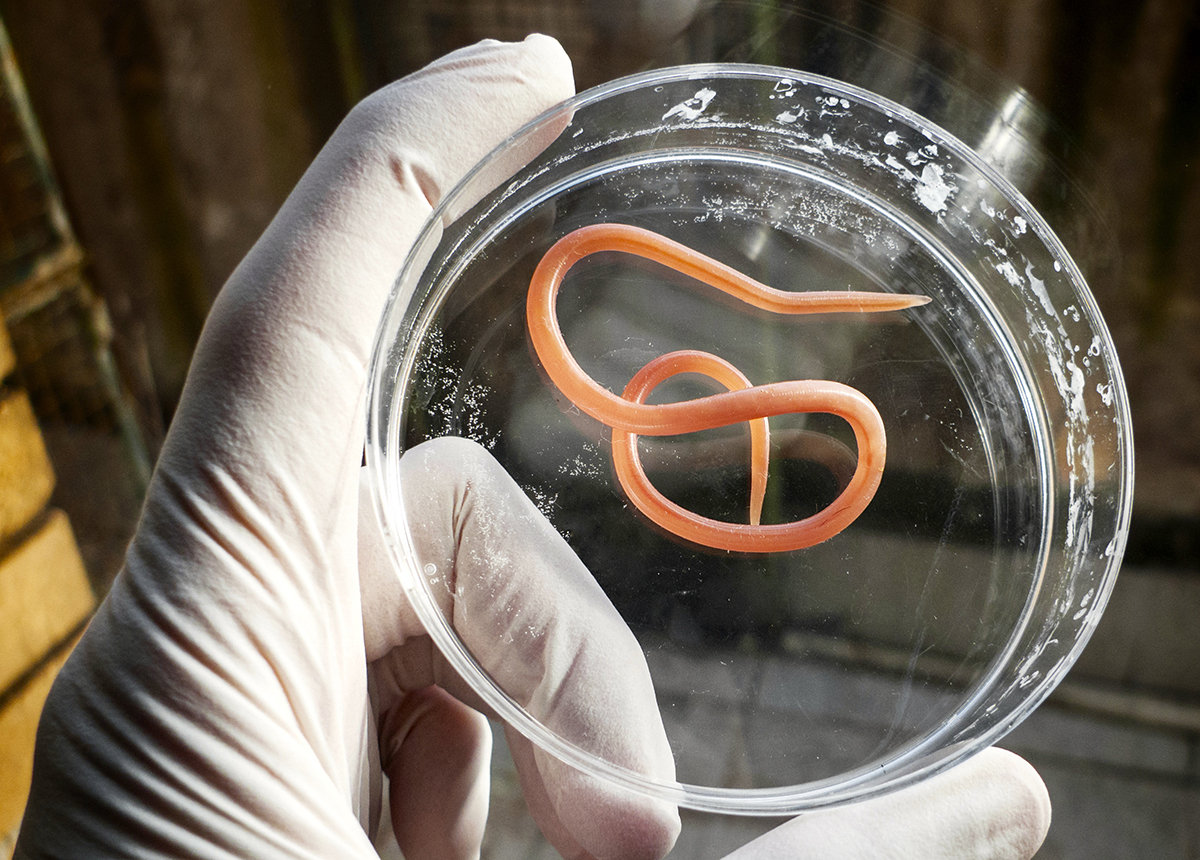
The larvaes drill into body and suck blood causing iron deficiency anemia.
Most nematodes such as tapeworms and whipworms are infected through eating food which contains their eggs. While hookworms are different from most nematodes. Hosts are affected by eating hookworm larvae’s or their larvae penetrating through skins. If it is not treated, hookworms can parasitise in the body for a long time, not just causing iron deficiency anemia, but also bringing the risk of heart failure.
The “hookworm” is a parasite that looks like a hook. The infected person will experience non-specific symptoms such as bloating, nausea, diarrhea, and sometimes blood in the stool, because hookworms has hook or plate teeth to bite intestinal mucosa.
Farmers or fishermen usually work barefoot, often exposed to contaminated water or mud and allow larvae get into their bodies. Once infected, the patient’s skin will show wavy blisters, like insects crawled lines, and the skin has itching as well as burning sensation.
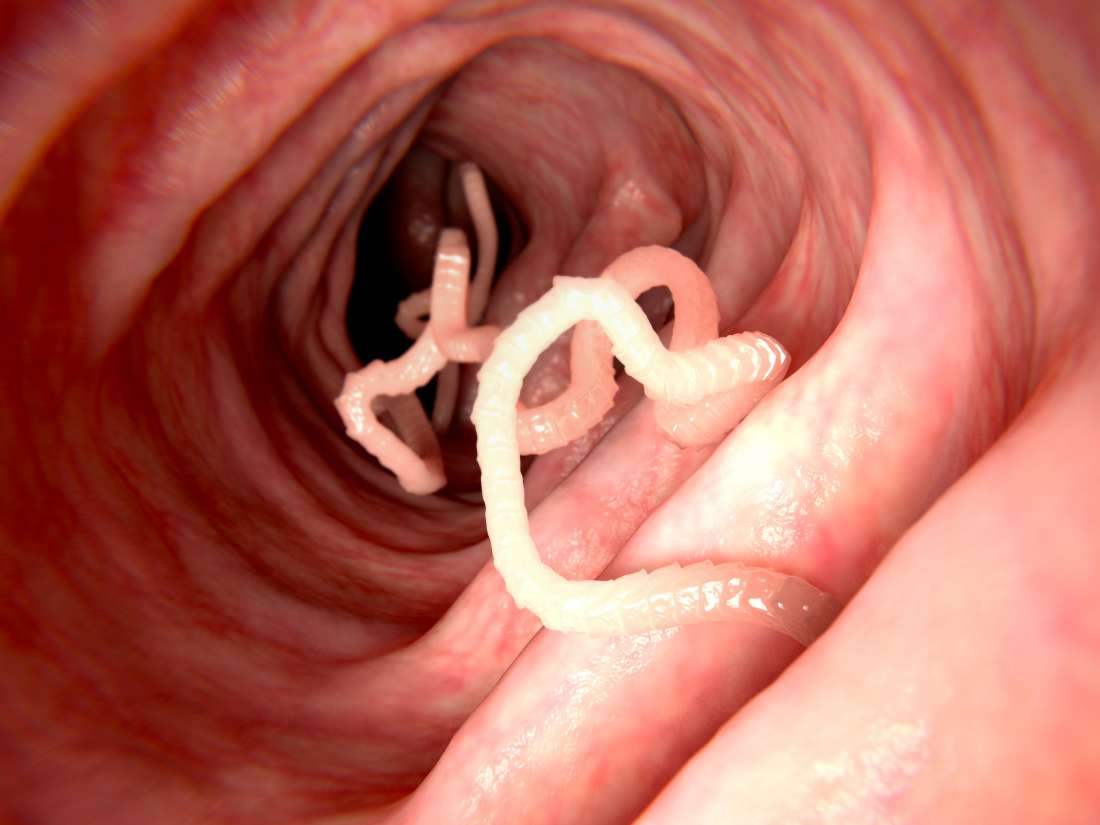
Medically this is known as “cutaneous larvae migrans”, caused by the larvae migration within skin tissues.
As larvae penetrating the skin, they will swim to small intestine, bite intestinal mucosa and suck blood, causing chronic blood loss to the host. Over time, irons and proteins continue to be depleted and lead to iron deficiency anemia.
Sometimes patients can have lower levels of hemoglobin because of malnutrition. If the symptoms of anemia become more severe and the heart muscle cannot pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs, the heart will “fail”.

Continuous eating of soil and paper –
Anemia induces pica
The normal human hemoglobin level is about 12 to 13 gm/dl. However, many hookworm-infected patients have hemoglobin value of only 4 to 6 gm/dl when admitted into hospitals and demonstrate some symptoms of heart failure. Heart failure does not happen overnight but is caused by long-term anemia or no treatment after hookworm infection.
Iron deficiency anaemia can also cause pica, a symptom of persistently taking non-nutritional substances, such as putting soils and papers into mouths.
If a child develops symptoms of pica, it is necessary for parents to let their children undergo blood tests to rule out anemia. If a patient is diagnosed with anaemia, he or she should be further investigated for the presence of medical conditions such as iron deficiency anemia and parasite infection.
It is recommended that people at risk of infection should wear waterproof boots when they contact dirt or wet areas or avoid infection-prone areas altogether.
Daily production of 10,000 eggs
When a whipworm infects and inhabits in intestinal tracts, it can cause more severe inflammation of the intestinal walls, resulting severe gastroenteritis, diarrhea, and even blood in the stool and anemia. The patient must be treated promptly to avoid deterioration of the health conditions.
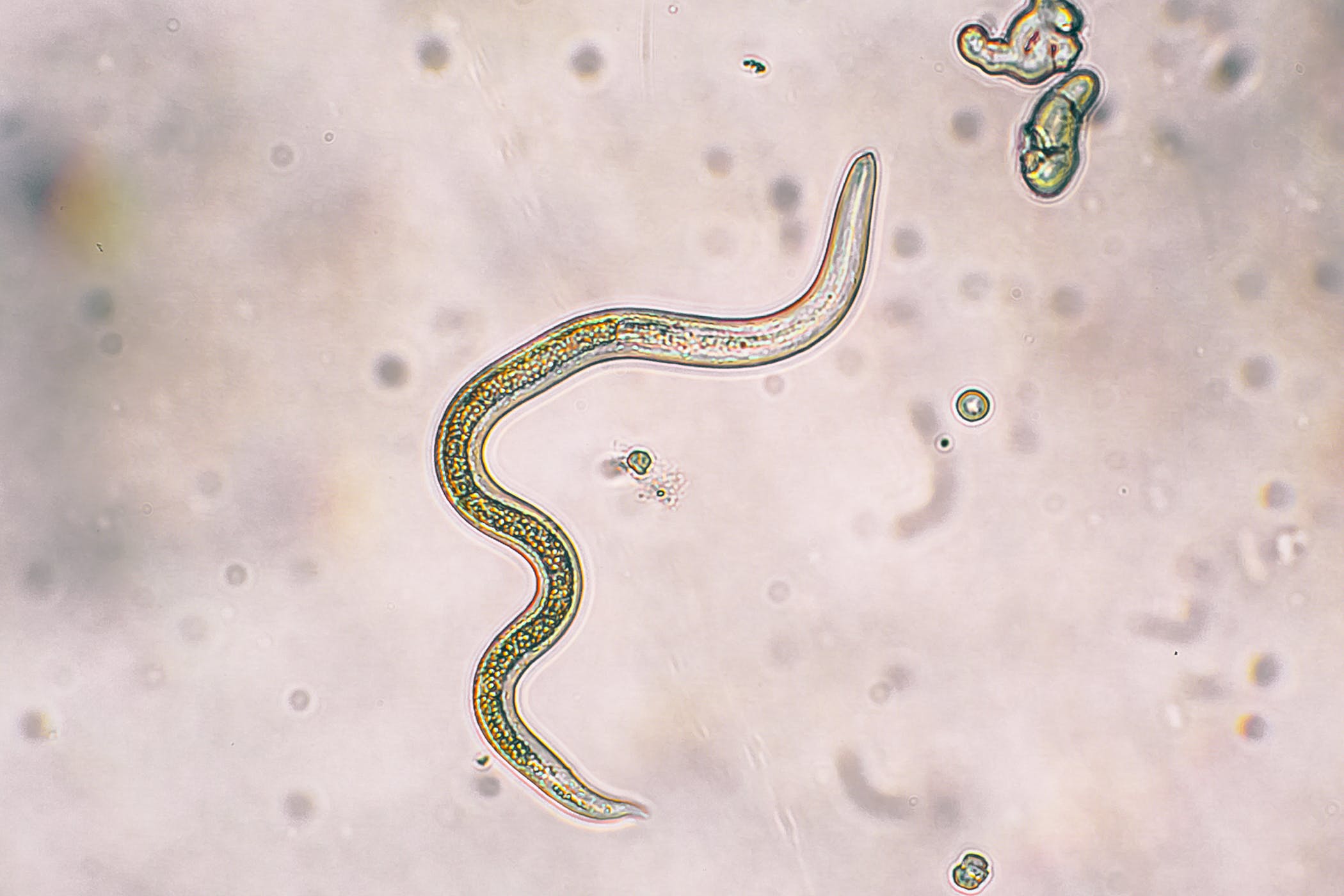
Like the infection of tapeworms, the patient was infected by eating the eggs. Normally female worms produce between 2,000 and 10,000 eggs per day, which takes two to three weeks to develop into infectious parasites.
Usually whipworms grow in the small intestine and swim into the large intestine to hide. The whipworm takes 3 months from egg to become adult with the lifespan of 1 year. The eggs of whipworm are lemon-shaped under the microscope.
Because whipworm infection can lead to frequent diarrhea, the patient may experience problems such as anal prolapse or rectal prolapse. If parents suspect that their children are infected and have related symptoms, they must seek treatment as soon as possible to eliminate whipworm infection. Long-term presence bloody stools can lead to anaemia. If the site of damage or bleeding is also the site of iron absorption within small intestine, then patients may face iron deficiency anaemia, which end up affecting the development of children.
If a sick child has symptoms of bloody stools and rectal prolapse, doctor will prescribe antibiotics to control the infection initially, thereafter faeces are taken for microscopic examination, and find out if parasite infection is taking place.
2-time treatment for killing parasites thoroughly
The way to kill nematodes is to take anti-parasitic drug – Albendazole, based on child’s body weight, that is, 20 milligrams per kilogram of prescription, the maximum volume is not more than 400 milligrams. The market is available with tablets and liquids, 200 and 400 mg respectively for the selection of patients.
Usually the child’s prescription is 200 milligrams, unless the child’s body size is larger, then the dosage can be raised to 400 milligrams, both pregnant women and breastfeeding people are recommended not to take this kind of medicine.
Children infected with tapeworms need to take medication twice. Medicine is taken on second time after two weeks when first-course of medicine is completed. It takes two weeks for tapeworms to develop from eggs to the adults, plus the given medicine is just killing tapeworms instead of their eggs. Therefore, two-course medical treatments are required, for eliminating these parasites completely.

If a child faces intestinal obstruction due to nematodes, doctor can no longer prescribe anti-parasitic drug because it can cause death of these parasites and aggravate intestinal obstructions further.
Usually, doctors prescribe antibiotics to control gastroenteritis of patients. If necessary, surgery will be done, and deworming medicine will be prescribed after about two weeks of surgery.
Questions & Answers
Question 1: Can probiotics help in preventing nematode infection or drive out the nematodes?
Little help.
Question 2: If a child has bloody stools, does it mean an infection of parasites or nematodes has happened?
Not necessarily. Blood in the stool can sometimes causing by bacterial infection or other diseases. Parents should take their children for further checking and consulting their doctors.
Question 3: Do deworming medicines need to be taken regularly every year to prevent infection?
Previously, children need to take such medicines regularly. Now this kind of medicine is only required when necessary. It is best to consult a doctor and get advice before taking this medicine.
Question 4: Many parents and schools advocate outdoor or nature-teaching activities. Should these activities be stopped to avoid being infected by parasites?
Parents should also consider the environmental hygiene and take preventive measures while allowing children to engage in outdoor activities or contact with nature.
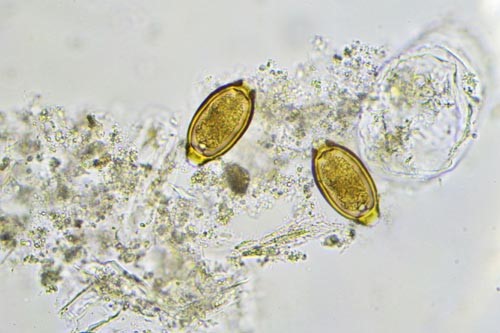
The eggs of the whipworm are lemon-shaped under the microscope.
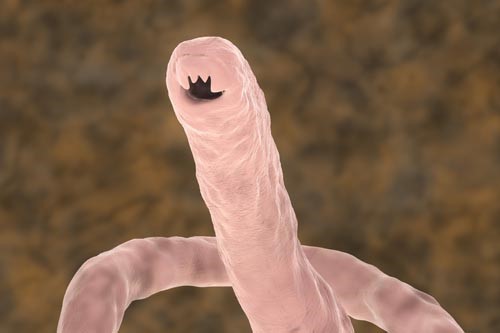
Hookworms have hook or plate teeth to bite the intestinal mucosa for food.