Stomach Acid Reflux / Heartburn
( Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease, GERD )
Case Study :
Susan is a career woman and mother of three children. Due to her busy schedules, very often she ends up turning her meal times upside down, eating irregularly, and feeling indigestion. Recently, she often complained on stomach pain. Although Susan has consulted a few doctors already, there was no sign of improvement. Eventually, she just went to pharmacy outlets and bought medicines directly for relieving her symptoms.
Last 2 weeks, her throat has been accumulating a lot of sputum, she could neither swallow nor spit it easily. After this symptom plaguing her for half a month, she decided to visit her doctor again. The doctor diagnosed her problem was caused by reflux of stomach acid.
She is a bit confused. What is reflux of stomach acid? How is stomach acid is produced? Does acid reflux bring serious medical complications? How can it be improved?

Alcohol, Smoking, Oily and Spicy food can aggravate the problem of stomach acid reflux.
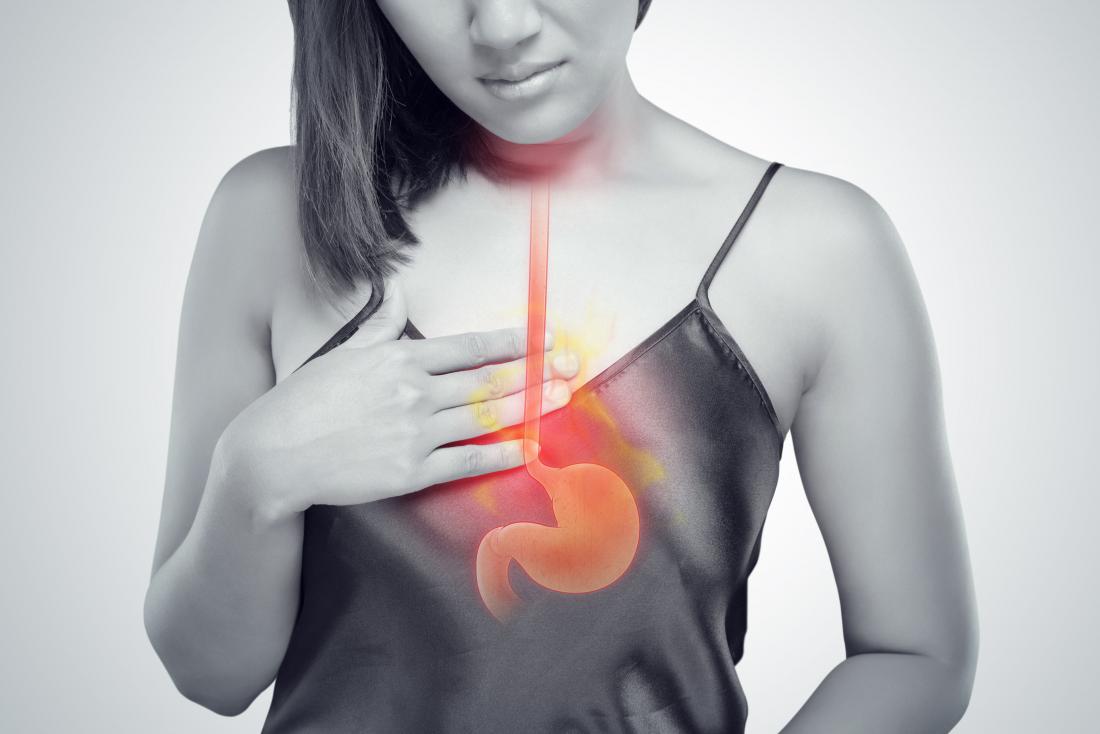
The main symptom of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is “heartburn”, meaning that acid reflux enters the oesophagus tube. The patient will feel a burning sensation from chest till mouth.
When stomach acid reflux back to the mouth or throat. Patients may face swallowing problems, often it is mistakenly assumed causing by sore throat and even heart attack. Other common symptoms of GERD include chest pain, cough, throat inflammation, inflammation of the vocal cords, hoarseness, asthma, and sleep disturbances.
After eating, food is transported down to oesophagus, and it will go through the stomach via a door called the “lower oesophageal sphincter”, which is a junction in between stomach and oesophagus. Usually this “door” is closed and it only opens automatically when we swallow food. When the muscle valve of this “door” relaxes and fails to function properly, there is a problem of reflux or backflow of gastric acid.
The main cause of muscle valve relaxation is genetic or dietary problems. Smoking, drinking, eating fast food, oily, spicy foods can also aggravate the problems of this disease.
Some patients are suffering GERD not solely due to relaxation of muscle valve, in fact, their disease happened partly because of excessive production of gastric acid or slow motility of stomach.
An increase of body weight will lead to higher production of stomach acid. Therefore, obesity is also an important risk factor of this disease. Obese people have higher abdominal pressure than normal people. Excessive body fat can exert pressure on the oesophagus. The crushing effect pushes stomach acid to the oesophageal tube.
The stomach has a protective layer that can protect the stomach wall from being damaged by stomach acid. However, the oesophageal tube does not have such protective layer. Once the stomach acid rises upstream, it can cause inflammation of the oesophagus tube and a burning sensation. This burning sensation sometimes makes the patient mistakenly believe that it is a heart attack because the heart locates just behind the oesophageal tube.
GERD is quite common disease, estimated about 15 to 25% of the world’s population suffering from this disease, and about 10% in the Asia Pacific region. According to local statistics, out of the 2,533 endoscopic cases, 7.93% of patients were diagnosed with acid reflux, with the Indian ethnic group accounting for the highest proportion of 38%, while the Chinese and Malay ethnic groups accounted for 28% and 34% respectively.
The prevalence of men and women is 56% and 44%, respectively, indicating that men are more prone to acid reflux than women. The proportion of elderly people aged 60 and above is 38.3%, and that of those aged 40 to 60 is 36.8%. This means that aging process can also increase the risk of GERD.
Elimination of Helicobacter Pylori Increases Incidence of GERD
Gastroenterology has found an interesting finding in recent years. When the Helicobacter pylori in the stomach are eliminated, the incidence of acid reflux in stomach is found increasing gradually. The reason for this inverse proportion is due to the fact that H. pylori causes gastritis (inflammation of stomach).
There are two kinds of gastritis, one type happens at the bottom of stomach, which leads to an increase in stomach acid, and subsequently leads to gastric or duodenal ulcers, that also explained why Helicobacter pylori is known as one of the main causes of stomach ulcers.
The other type of gastritis is causing inflammation in the entire stomach, which decrease the production stomach acid instead. When Helicobacter pylori is eliminated, it leads to higher production of gastric acid, thus increasing the incidence of acid reflux.
It is worth noting that GERD is not a stomach disease per se because it occurs in oesophageal tube so it is a disease of the oesophagus. Therefore, GERD cannot be regarded as gastric problem nor disease.
Generally, GERD is considered a very mild disease in the Asia-Pacific region, hence it can be treated effectively by using medications. At present, the main treatment is proton-pump inhibitor (PPI) or hydrogen receptor blockers. The effect of this drug on reducing gastric acid secretion is considered highly effective.
These drugs include esomeprazole, omeprazole, lansoprazole, pantoprazole, rabeprazole, dexlansoprazole, and the like.
If GERD happens but it is taken lightly and not treated at all, serious complications will occur. For example, severe oesophageal tuberculosis, long-term inflammation leading to narrowing of the oesophageal tube, obstruction of the oesophagus tube, and change of its cells due to long-term disturbance of the oesophageal tube and increase the risk of oesophageal cancer.

How to diagnose a stomach problem?
Very often, patients will say: “Doctor, I have ‘gastric’”. In fact, this is an incorrect description. Gastric is not a symptom nor illness. It is just an adjective that describes stomach.
The medical term for gastric pain is called dyspepsia, which means indigestion, epigastric pain, upper abdominal distension, early fullness, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, and other epigastric discomfort.
There are many causes of upper abdominal pain, including stomach ulcer, stomach inflammation, stomach cancer, and cholelithiasis pancreas or liver problems are all possible causes. The patients should describe the symptoms with more details and avoid prejudging, so they can assist their doctors in determining the final diagnosis.
Under what circumstances do you need to use a gastric endoscope? Is there any risk?
Gastroscopy and extraction of tissue are generally safe, but patients should also understand that all invasive procedures have their own risks, but this risk is not significant. It takes only 5 to 10 minutes to finish the test. Doctors are going to judge the necessity of this test based on the presence of high-risk symptoms (such as oesophageal stomach and duodenal bleeding, vomiting, recurrent vomiting, difficulty swallowing or swallowing pain, loss of weight, etc.).
8 Ways To Reduce Stomach Acid Reflux ( GERD )
- Avoid acidic, spicy and oily foods
- Higher frequency of meals, but eat with smaller quantity
- No meal before sleeping
- Reduce body weight
- Less alcohol or beverages containing caffeine, especially red wines
- Wear loose-fitting clothes and less-tight belt, so stomach is not constricted.
- Stop smoking
- Elevate bed, raising head of bed six to eight inches, so gravity keeps gastric acid down in stomach.