Poisoning is not disease.
Nine first-aid methods to save lives

About poisoning incidents, quite often elders and young children are the most common victims. Hence everyone should understand first-aid of poisoning, so that appropriate emergency treatment can be done timely. This is a critical step to save valuable lives.
From a medical point of view, poisoning is not an illness. It happens because of certain toxic foods or excessive drugs. After poisoning, when a poisoned victim suffers acute illness, coma, or even on the verge of death, what can we do then?
According to the death statistics of Malaysia in 2007, the number of deaths caused by poisoning was 35.88 in every 1,000 hospitalisations. Many people may ask what does poison means?
These are the common examples – foods such as certain wild herbs; excessive anti-hypertensive drugs, painkillers or other strong western medicines. toxic gases such as coal gas; herbicides, insecticides, and metals like lead and mercury.
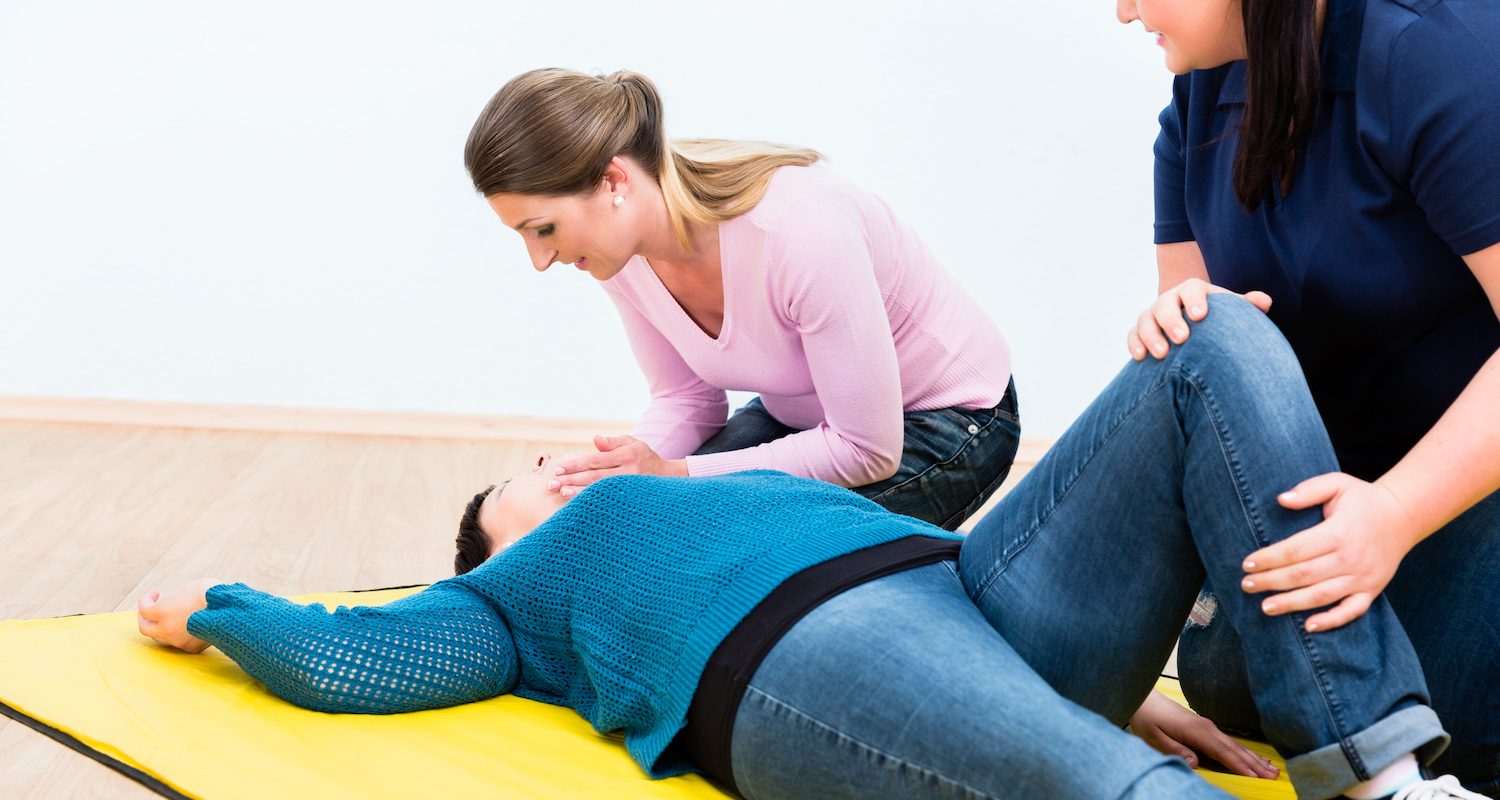


Different Poisoning First-aid Methods
1. Food poisoning
- Try to get rid of toxic foods in the stomach, such as gastric lavage.
- Intravenous therapy.
- Supply oxygen.
- Give the patient antidotes.
Antidotes are other type of drugs that can detoxify certain drugs. In fact, not every poisonous food or gas has its antidote to neutralize the poisonous effects. Most poisons with antidote are drugs, such as heroin and methamphetamine.
2. Drugs Poisoning
- Ordinary first aid: when poisoned person is awake, then victim can drink plenty of water to dilute the poison; or drink plenty of milk to protect the digestive system and slow down the rate of poison absorption. Get medical advice as soon as possible.
- Corrosive Toxic Aid (strong acid, strong alkaline): do not induce vomiting, do not attempt any dilution, do not neutralize; do not give victim anything to eat; keep the airway open; prevent shock; seek medical advice as soon as possible.
- If the lips burn, do not induce vomiting, dilution or neutralization.
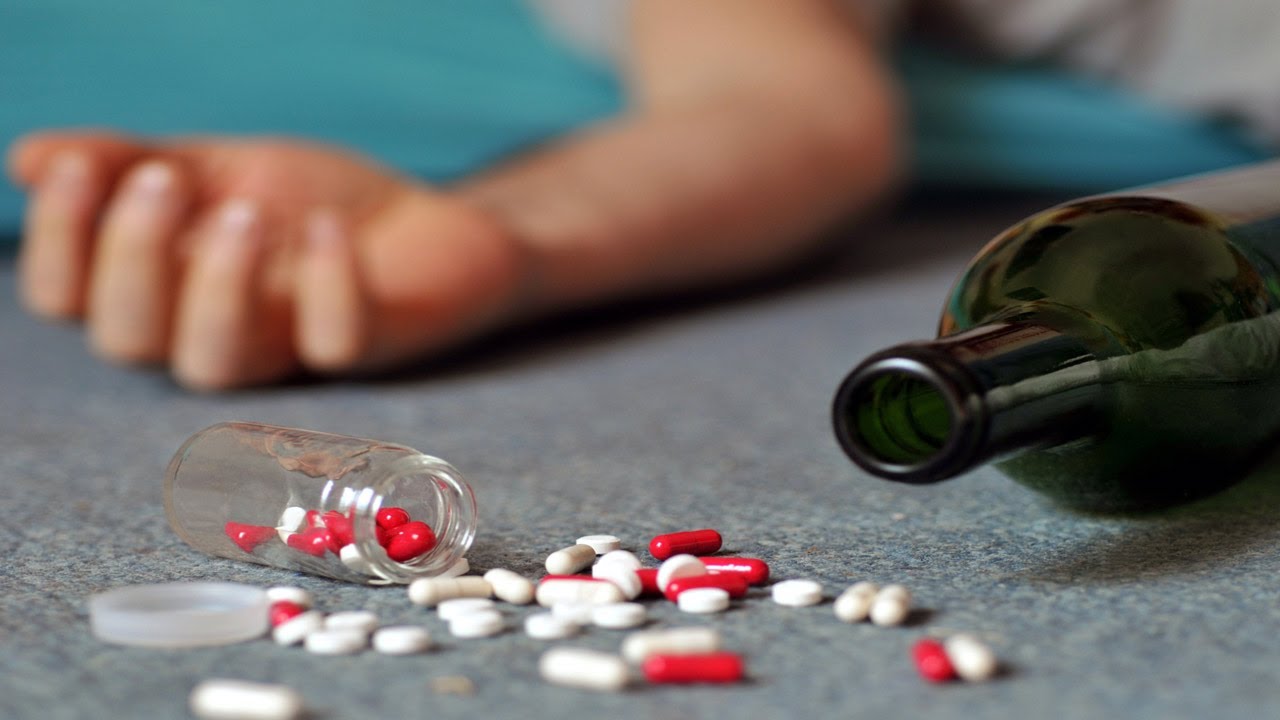

3. Gas poisoning
- Cover mouth and nose to open doors and windows and turn off the gas main switch.
- If enter deep pits and deep wells to save people, must pay attention to safety.
- Raise the victim to a ventilated place, make him rest and release the restraint of breathing.
- If the victim’s breathing stops, artificial respiration is applied.
- Check and handle other injuries.
- Keep warm and get a doctor immediately.
4. Snake bites
- Keep calm and discern the shape, colour and characteristics of the snake.
- If cannot identify whether it is a toxic or nontoxic snake, treats it as poisonous snake bite.
- remove the restraints, reduce the activity, lower the injured limb to avoid blood backflow, resulting the swelling of injured limb.
- bandage with elastic bandage, the larger the area the better.
- remember bite marks and injuries symptoms.
- As soon as possible send victim to see a doctor, injection of anti-venom, tetanus vaccine.
- Do not believe in witchcraft or secret recipes, delay treatment, and endanger life.
- Do not cut open wounds; do not apply ice on wounds; do not drink stimulating beverages.
- Do not use a tourniquet or compression belt.
Regular treatments in hospitals
- Some people must stay in hospital after being poisoned.
- The doctor must try to care for the main organs of the patient such as the respiratory system, blood pressure, body temperature and heart rate.
- Try to eliminate substances that cause poisoning to the patient.
- Provide patients with antidote to eliminate toxins.
- Most of the toxins that the liver dissolves must be excreted in the urine.
- If the patient feels drowsy and tired, the doctor will use a breathing catheter to reach his ventilator to help him breathe and prevent vomiting.
- If the patient has a high fever, should control feverish condition by using an ice pack to rub patient’s body and lower his fever.
- Gastric Lavage: In the past, doctors usually cleaning out the contents of stomach for eliminating toxins. However, at present, this treatment is rarely used because it can only eliminate very small amounts of toxins, moreover it can also cause serious complications.
- Activated Charcoal: If a poisoned person comes to the hospital, the doctor sometimes gives activated charcoal, it is a kind of black pill that can be combined with poison so that poison does not flow into the bloodstream from the stomach.
Problems that encountered by doctors
When a poisoned patient is admitted to a hospital, the doctor is likely to face the following problems, such as:
- Do not know how the patient is poisoned.
- The doctor cannot make the right response as soon as possible.
- Doctors do not know what type of treatment to give to poisoned patients.
Use physical examination to diagnose the cause of poisoning
In order to find the exact cause of poisoning in a short period of time, the doctor will perform a physical examination on the patient, including blood pressure, pulse rate, respiratory rate, body temperature, dehydration assessment, and abdominal examination. If doctors suspect other poisoning problems, abdominal CT scans or X-rays, and even blood tests, are needed to make the correct diagnosis.
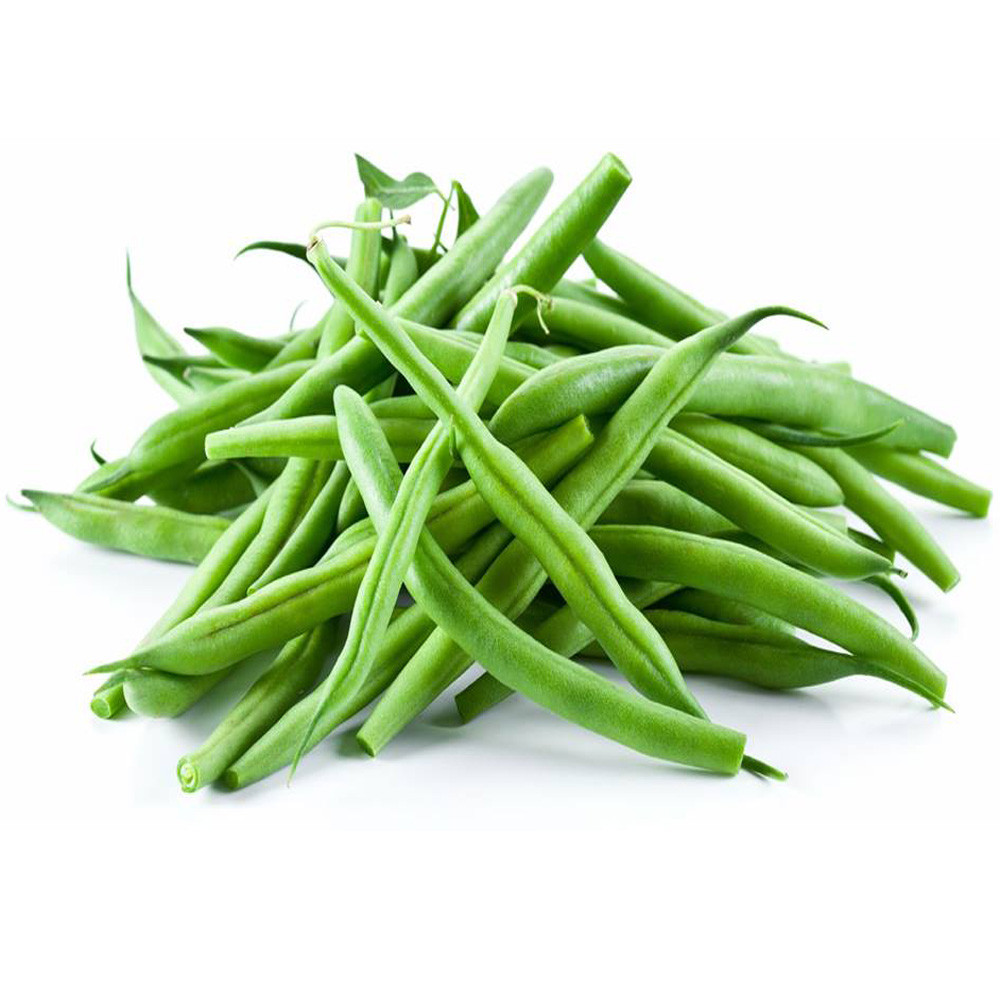


Green beans. Don’t eat raw type
Contains nitrite and trypsin. After eating raw, it has a strong stimulatory effect on the gastrointestinal tract and can cause gastroenteritis. Therefore, the green beans also need to be fully cooked to be edible.
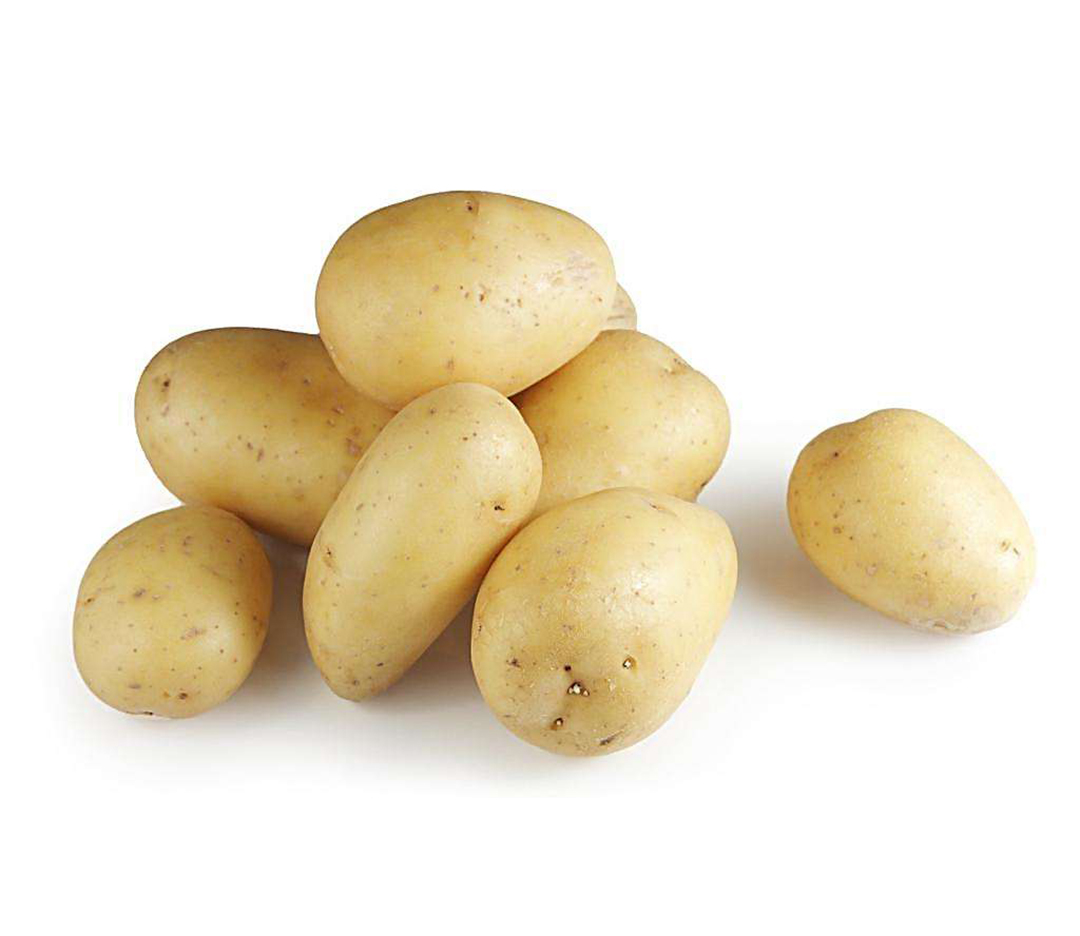

Do not eat sprouted potato
Containing solanine, after eating sprouted, greenish, rotted potatoes will cause throat itching, acute gastroenteritis, severe cases may also cause hemolytic jaundice.
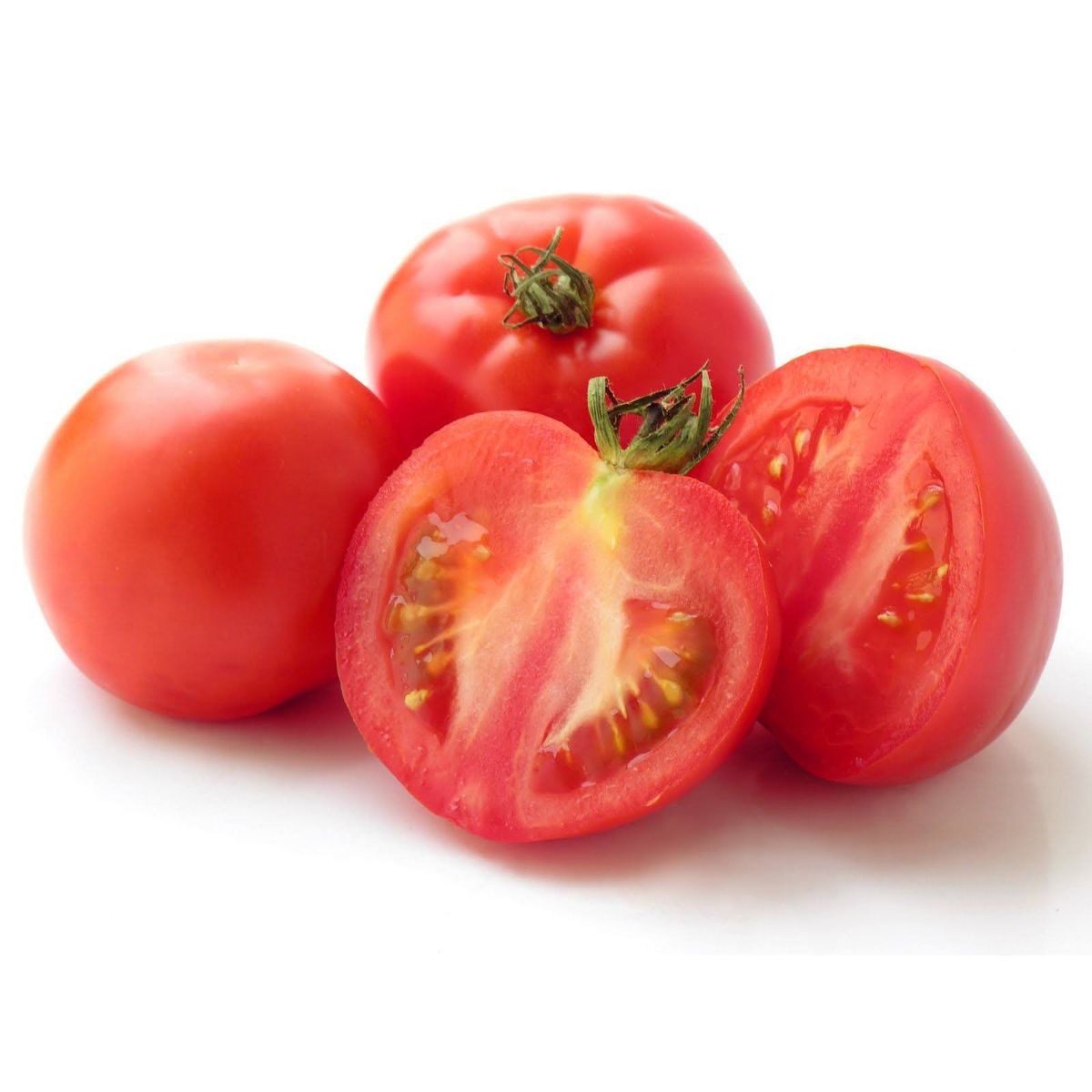

Do not eat unripe tomato
Cannot eat unripe tomato, it contains a lot of solanine, with the same toxicity of the sprouting potato, causing nausea, vomiting, dizziness, runny nose and other poisoning effects after eating.

Pumpkin
Do not keep for too long