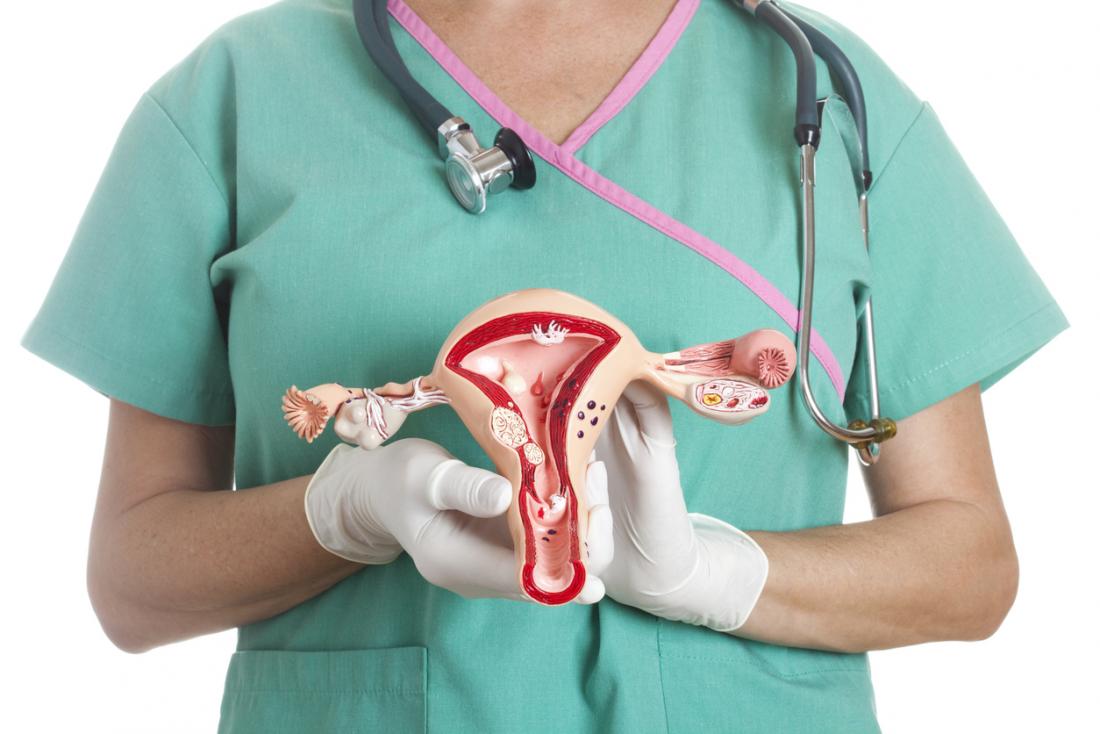
Menorrhagia / Excessive Menstrual Bleeding
Question: My mother is 49 years old woman. Her menstrual period has recently been reduced from the previous 5 days to 3 days. Her menstrual blood volume has also been increasing compared her younger age. She describes toilet bowl was turned into “red sea”. Before that, her menstrual blood was coagulated-type only. Is this condition can be regarded as normal?
Under the normal circumstances, women’s menstrual blood volume is about 50 ml to 80 ml, and the amount of blood loss is highest on 2nd to the 3rd day, and entire cycle lasting about 5 to 7 days. Menstruation is caused by the detachment of the endometrium and bleeding, because of changes during ovarian cycle.
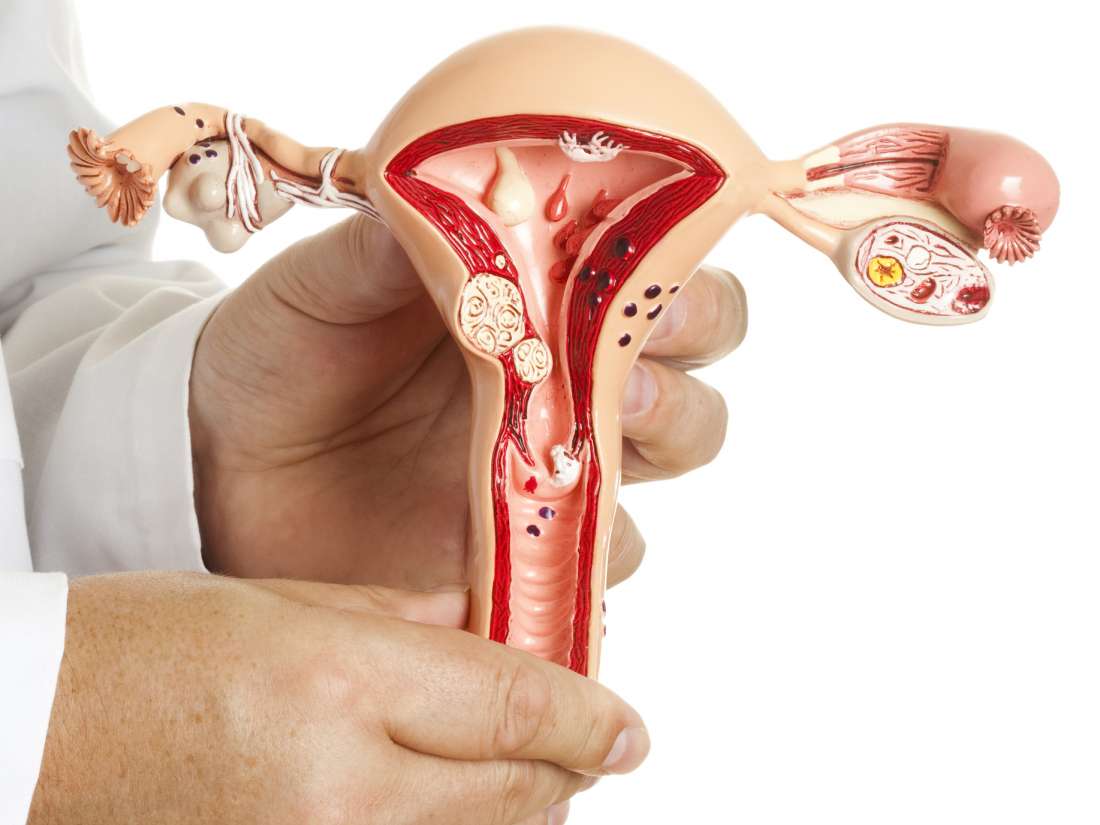
If the daily blood loss is more than 80 ml, or the amount of menstrual blood is obviously higher than before, it is also called menorrhagia. The presence of menorrhagia together with blood clots, are considered as manifestation of menstrual incoordination.
If the area of the endometrium detachment is large, or abnormal constriction of blood vessels happening in uterus, then blood clots will be produced, which is a normal physiological phenomenon. Occasionally, there are blood clots found in menstruation once awhile, which is not a problem to the health. However, if there are continuous and excessive menstrual bleeding and blood clots, it is necessary to seek medical advice promptly to identify the root cause of the medical conditions.
Question :
Why the amount of menstrual blood is higher compared to younger days?
The common reasons of excessive menstrual bleeding are listed below:
- Dysfunctional uterine bleeding – abnormal genital tract bleeding based in uterus and found absence of demonstrable structural or organic disorders. Often manifested as irregular menstruation, excessive menstruation, prolonged menstrual period, severe bleeding and other symptoms. This is usually more common at puberty or near menopause.
- Uterine fibroids – This is a common genital growth in women of childbearing age with an incidence of 10% to 30%. Menorrhagia is more common in two types of uterine fibroids, intramural and submucosal.

In this situation, oral medication control is not effective and may require surgery.
- Pelvic inflammatory disease – This is a common cause of abnormal vaginal bleeding. When inflammation occurs, the local blood vessels become fragile, and menstrual bleeding does not easily coagulate, which often leads to increased blood volume and prolonged menstruation.
- Endometriosis – Endometriosis, especially uterine adenomyoma, interferes with various normal functions of the reproductive organs, often accompanied by symptoms such as prolonged menstruation and excessive menstrual blood.
- Hematopathy – Some blood diseases affect clotting, such as thrombocytopenia, hemophilia, leukemia, and aplastic anemia, and may also cause menstrual flow problems.
- Inappropriate contraception methods – IUDs and birth control rings are commonly used contraceptive methods. The most prominent problems that arise are the marked increase in volume and bleeding.
- Others – Changes in weather and seasons, changes in the living environment, emotional stress, excessive fatigue, and irregular diets are all reasons for excessive menstrual flow.